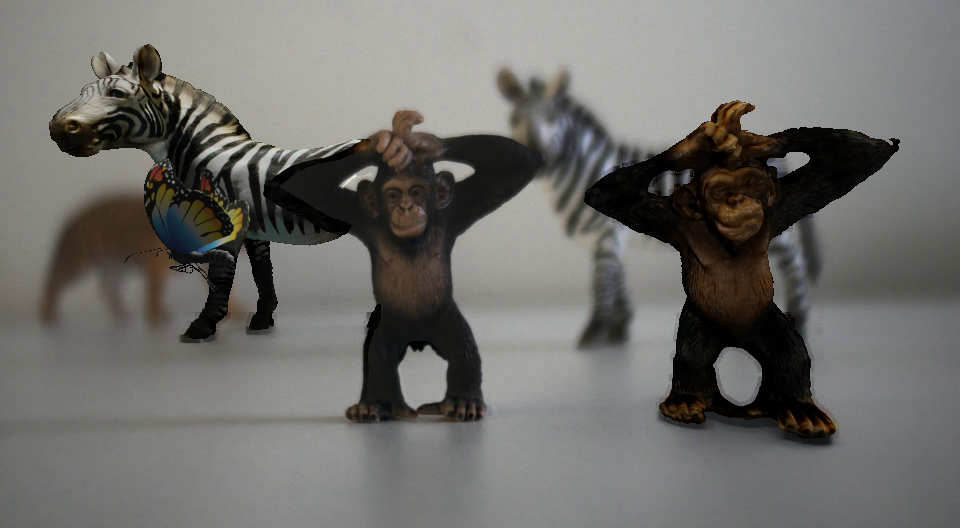
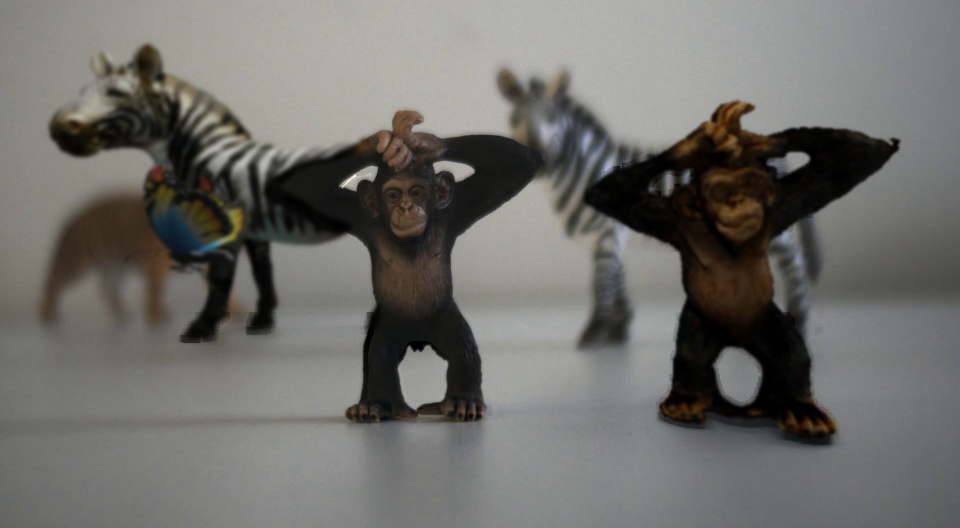
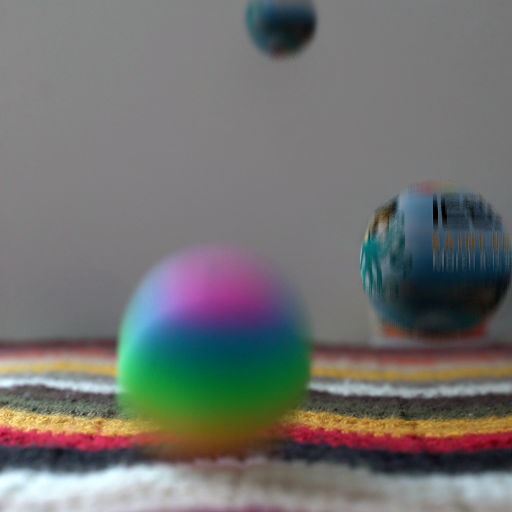
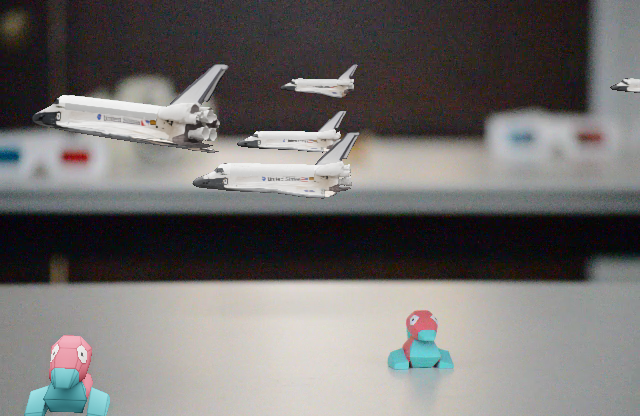
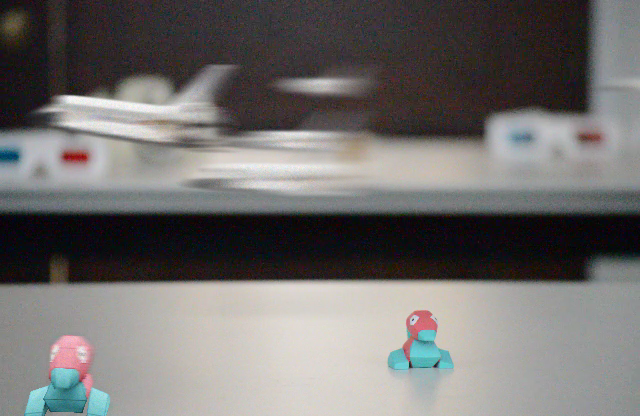
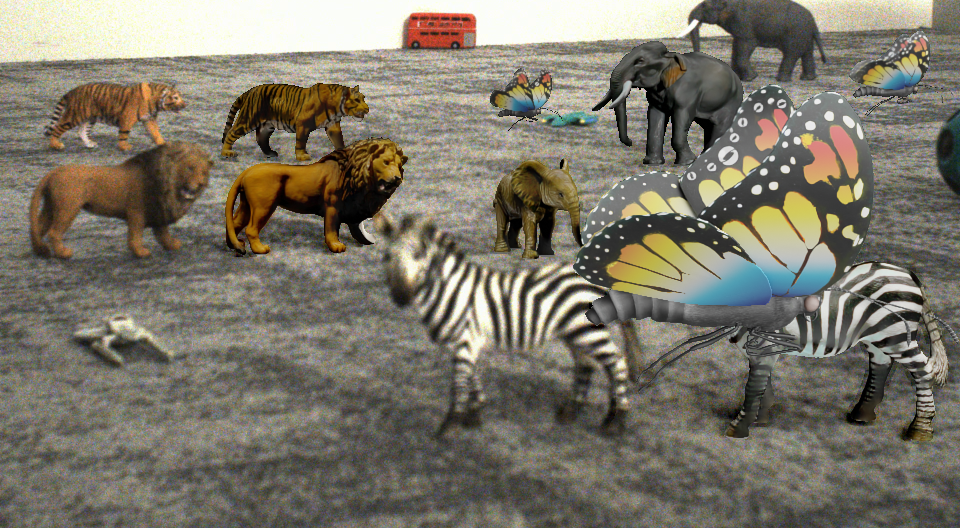
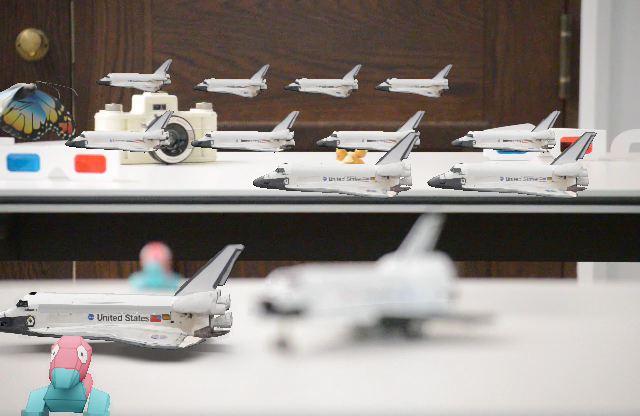
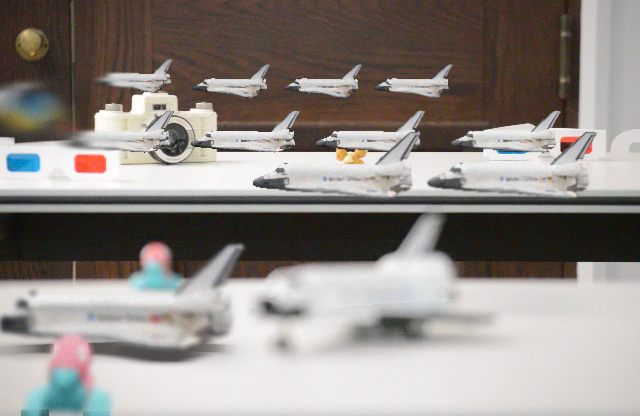
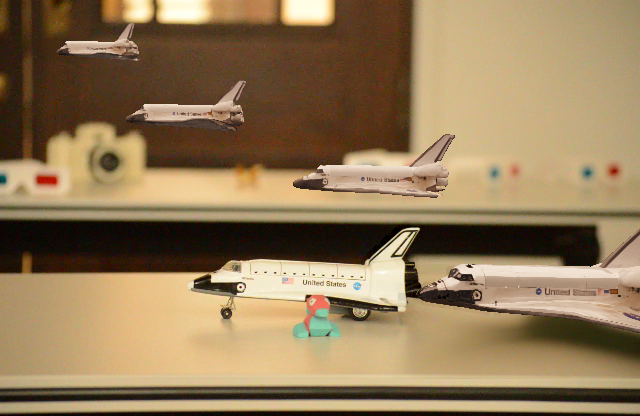
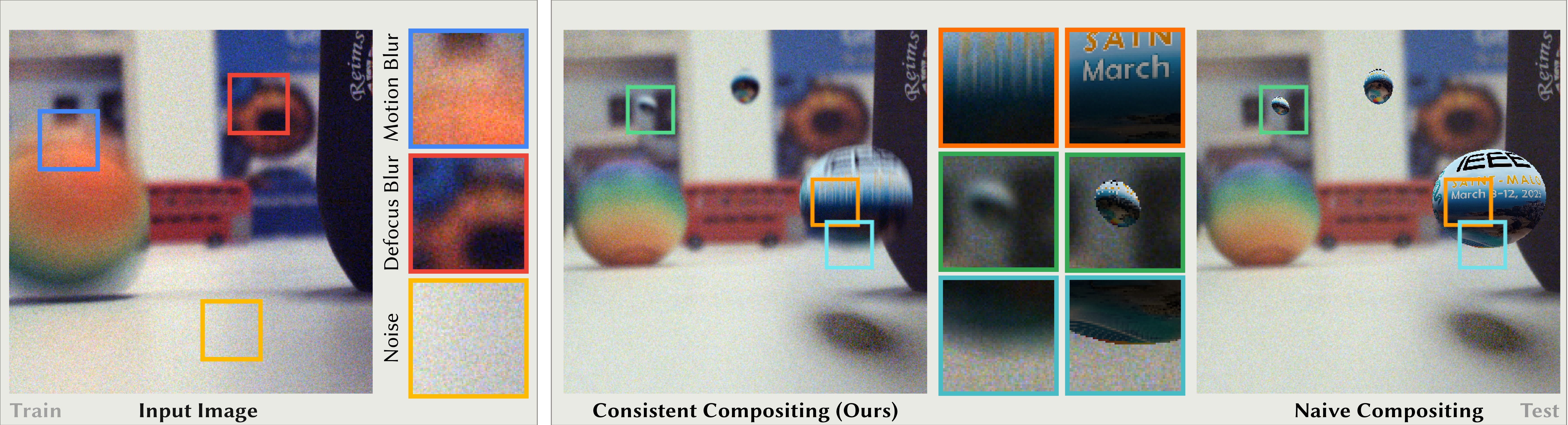
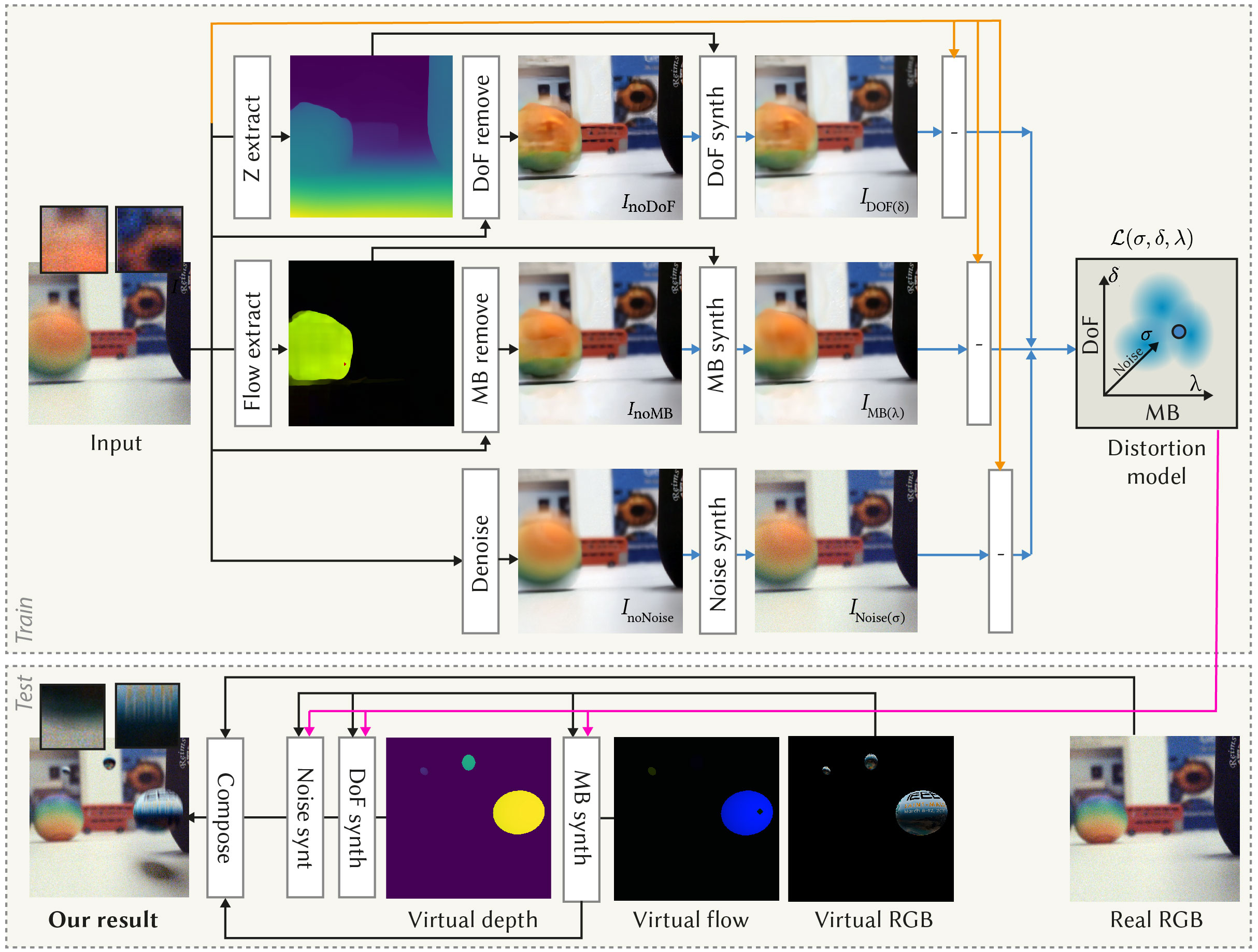
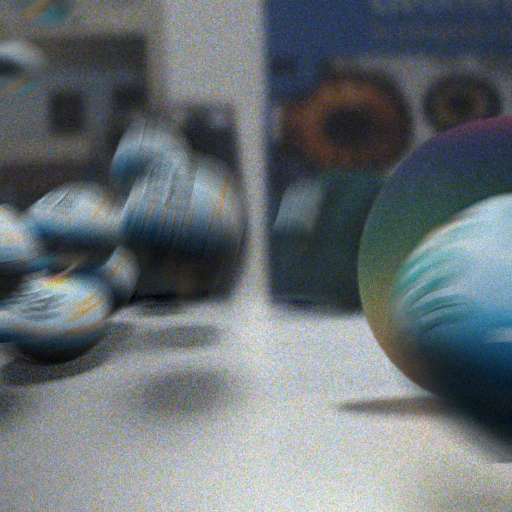Consistent Compositing (Ours) vs Naive Compositing
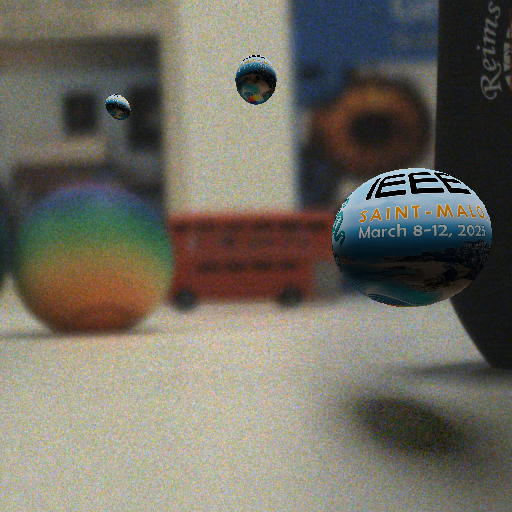
Naive Compositing
Consistent Compositing (Ours)